Securing the BusinessObjects Adapter
There are two types of users associated with the BusinessObjects Adapter, Runtime Users and Schedulers. You maintain definitions for both types of users from the Users pane.
-
Runtime Users
Runtime users in the context of BusinessObjects jobs represent those users and passwords required for authentication. BusinessObjects operations require authentication against a valid BusinessObjects user as defined by a BusinessObjects administrator. You can also use runtime users to override data source logons used by your reports. See Defining Runtime Users.
-
Schedulers
Schedulers are those users who will define and manage BusinessObjects jobs. There are three aspects of a user profile that grant and limit access to scheduling jobs that affect BusinessObjects:
Security policy that grants or denies add, edit, delete, and view capabilities for BusinessObjects jobs.
Authorized runtime user list that grants or denies access to specific authentication accounts for use with BusinessObjects jobs.
Authorized agent list that grants or denies access to specific BusinessObjects Adapter connections for use when defining BusinessObjects jobs.
See Authorizing Schedulers to Work with BusinessObjects Jobs.
Note: If you are using WinAd or LDAP authentication, see Using WinAD or LDAP Authentication.
Defining Runtime Users
The credentials specified for the runtime user are used to store the information about the simple user security context consisting of a user name and password pair and to pass this information to the adapters. This runtime user can be used for database targets when needing database authentication.
The Runtime User for BusinessObjects must have these user access rights:
-
View and Edit Objects rights for Info Objects
-
View Objects right for server CentralManagementServer
To define a runtime user:
-
Expand the Administration node from the Navigator pane and click Runtime Users to display the defined users.
-
Right-click Runtime Users and choose Add Runtime User from the context menu (Insert mode).
OR
You can also right-click a user in the Runtime Users pane and choose Edit Runtime User from the shortcut menu (Edit mode).
Note: If this is a new user definition, enter the new user name in the User/Group Name field.
-
Enter the Full Name or description associated with this user.
-
Click the Domain field and enter a valid BusinessObjects authentication method.
Example: Enterprise or WinAD.
-
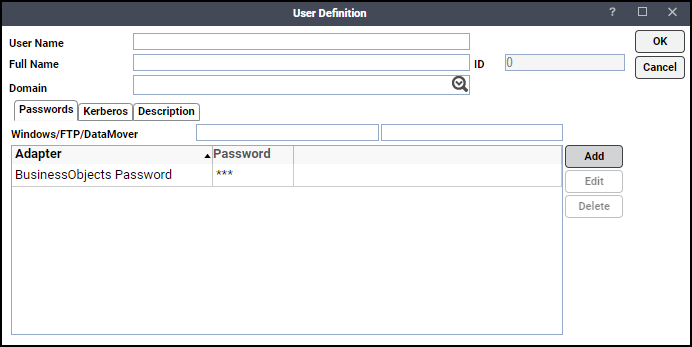
Click Add on the Passwords tab to define this user as a runtime user for BusinessObjects jobs.
-
Choose BusinessObjects from the Password Type list.
-
Enter a password (along with confirmation) in the Password/Confirm Password fields.
Only those users with a password specified for BusinessObjects will be available for use with BusinessObjects jobs. The password might be the same as the one specified for Windows/FTP jobs.
Note: The password cannot be blank.
Note: If you have updated the passwords and are experiencing issues with running jobs or events, we recommend disabling and re-enabling the connection to ensure everything works properly.
-
Click OK to return to the User Definition dialog. The new password record displays on the Passwords tab.
-
Click OK to add or save the user record in the TA database.
Authorizing Schedulers to Work with BusinessObjects Jobs
There are three procedures you need to perform to authorize schedulers to work with BusinessObjects Jobs:
-
Authorizing Schedulers
-
Granting Access Privileges
-
Defining Scheduler Users
Authorizing Schedulers
To authorize Schedulers:
-
Click Administration > Security Policies to display the Security Policies pane.
-
Right-click Security Policies and choose Add Security Policy from the context menu. You can also right-click to choose an existing security policy in the Security Policies pane and click Edit Security Policy.
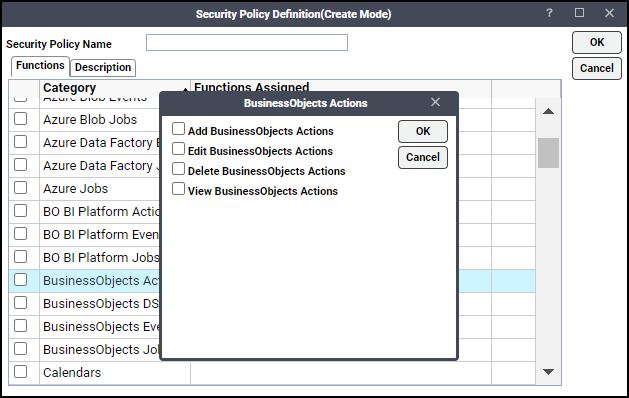
The three categories associated with BusinessObjects:
-
BusinessObjects Jobs
Add BusinessObjects Jobs – The ability to create new BusinessObjects jobs.
Edit BusinessObjects Jobs – The ability to modify existing BusinessObjects jobs.
Delete BusinessObjects Jobs – The ability to delete existing BusinessObjects jobs.
View BusinessObjects Jobs – The ability to view existing BusinessObjects jobs.
-
BusinessObjects Events
Add BusinessObjects Events – The ability to add new BusinessObjects events.
Edit BusinessObjects Events – The ability to edit existing BusinessObjects events.
Delete BusinessObjects Events – The ability to delete BusinessObjects events.
View BusinessObjects Events – The ability to view BusinessObjects events.
Suspend Monitoring – The ability to suspend the operation of the BusinessObjects monitor.
Resume Monitoring – The ability to resume the operation of the BusinessObjects monitor.
-
BusinessObjects Actions
Add BusinessObjects Actions – The ability to create new BusinessObjects actions.
Edit BusinessObjects Actions – The ability to edit existing BusinessObjects actions.
Delete BusinessObjects Actions – The ability to delete BusinessObjects actions.
View BusinessObjects Actions – The ability to view BusinessObjects actions.
Note: Refer to the Tidal Workload Automation User Guide for a general discussion on setting up security policies that you associate with Scheduler Users.
-
Granting Access Privileges
To grant access privileges:
-
Click Security Policies to display the Security Policies pane.
-
Click a security policy for the BusinessObjects job, event or action privileges and double-click on it to display its Security Policy Definition dialog.
-
Scroll down the list of function categories and double-click on the BusinessObjects category to display the available functions.
-
Choose the desired job privileges, then click OK.
A check mark appears next to the BusinessObjects function category indicating that one or more functions are selected within the category.
If needed, different security policies with varying authorized functions can be created to provide different levels of access for a variety of users.
Defining Scheduler Users
To define a Scheduler user to work with BusinessObjects jobs:
-
Click Administration>Interactive Users folder to display the Users pane.
-
Either click Add in the toolbar, or right-click in the Users pane and choose Add Interactive User from the context menu to display the User Definition dialog.
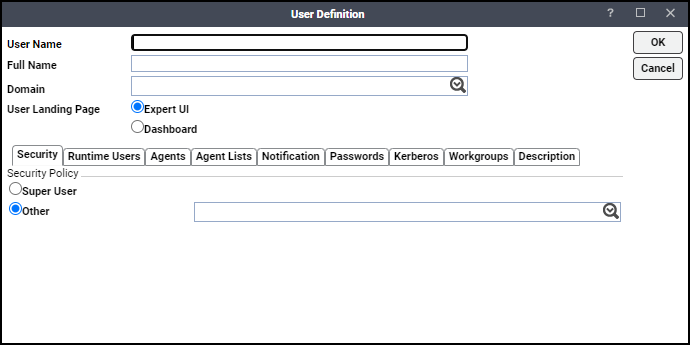
Note: If this is a new user definition, enter the new user name in the User/Group Name field.
-
Enter the Full Name or description associated with this user.
-
Click the Domain field, choose a Windows domain associated with the user account required for authentication, if necessary.
-
Click the Security tab, and then Other. Choose the security policy that includes authorization for Business Object jobs.
-
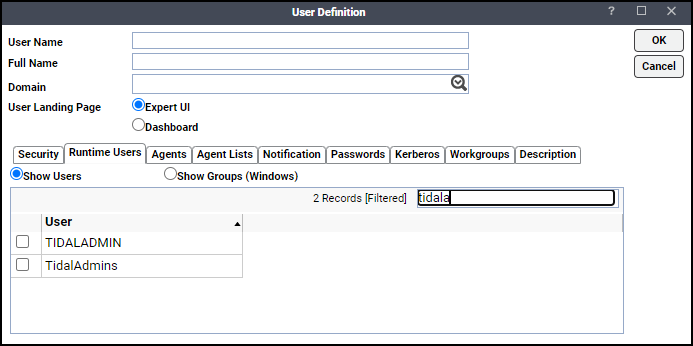
Click the Runtime Users tab.
-
Click the BusinessObjects users that this scheduling user can use for BusinessObjects authentication from BusinessObjects jobs.
-
Click the Agents tab.
-
Choose the checkboxes for the BusinessObjects connections that this scheduling user can access when scheduling jobs.
-
Click OK to save the user definition.